

- #Local network file sharing manual
- #Local network file sharing software
- #Local network file sharing series
- #Local network file sharing mac
Until its decline in 2004, Kazaa was the most popular file sharing program despite bundled malware and legal battles in the Netherlands, Australia, and the United States. The Audiogalaxy Satellite client grew in popularity, and the LimeWire client and BitTorrent protocol were released. This drove users to other P2P applications and file sharing continued its exponential growth. Shortly after loss in court Napster has been shut down to comply with court order. In July 2001, Napster was sued by several recording companies and lost in A&M Records, Inc. The network was proprietary and encrypted, and the Kazaa team made substantial efforts to keep other clients such as Morpheus off of the FastTrack network. Its FastTrack network was distributed, though unlike gnutella, it assigned more traffic to 'supernodes' to increase routing efficiency.
#Local network file sharing mac
In 2001, Kazaa and Poisoned for the Mac was released.
#Local network file sharing software
In September the eDonkey2000 client and server software was released. In July, Freenet was released and became the first anonymity network. In the gnutella network, all connecting software was considered equal, and therefore the network had no central point of failure. Gnutella, released in March, was the first decentralized file sharing network. Gnutella, eDonkey2000, and Freenet were released in 2000, as MP3.com and Napster were facing litigation. Napster provided a service where they indexed and stored file information that users of Napster made available on their computers for others to download, and the files were transferred directly between the host and client users after authorization by Napster.
Many P2P products will, by their very nature, flunk this requirement, just as Napster did. In the case of Napster, an online service provider could not use the "transitory network transmission" safe harbor in the DMCA if they had control of the network with a server. It is generally credited as being the first peer-to-peer file sharing system. In June 1999, Napster was released as a centralized unstructured peer-to-peer system, requiring a central server for indexing and peer discovery. MP3.com offered music by unsigned artists, and grew to serve 4 million audio downloads daily. In 1998, MP3.com and Audiogalaxy were established, the Digital Millennium Copyright Act was unanimously passed, and the first mp3 player devices were launched. The mp3 encoding, which was standardized in 1991 and which substantially reduced the size of audio files, grew to widespread use in the late 1990s. Internet Relay Chat (1988) and Hotline (1997) enabled users to communicate remotely through chat and to exchange files. Computers were able to access remote files using filesystem mounting, bulletin board systems (1978), Usenet (1979), and FTP servers (1985).
#Local network file sharing manual
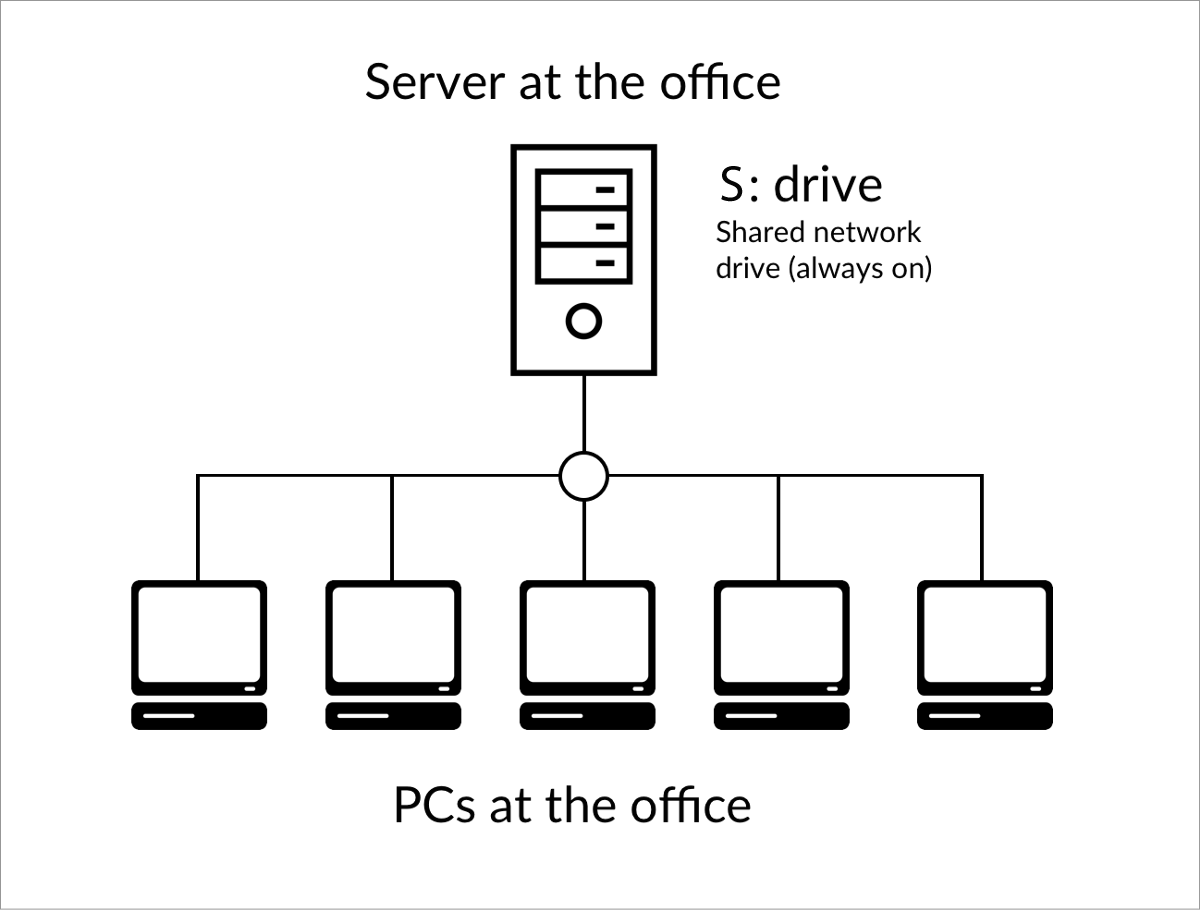
Common methods of storage, transmission, and distribution used in file sharing include manual sharing using removable media, centralized servers on computer networks, World Wide Web-based hyperlinked documents, and the use of distributed peer-to-peer networking (see peer-to-peer file sharing).įiles were first exchanged on removable media. It may be implemented through a variety of ways.
#Local network file sharing series
Part of a series onįile sharing is the practice of distributing or providing access to digitally stored information, such as computer programs, multimedia (audio, images, and video), documents, or electronic books. For printer and file sharing as local area network service, see shared resource. This article is about file sharing over the Internet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
